Overview
A Battery Management Unit (BMU) is a critical component in a battery management system (BMS), responsible for overseeing the performance and safety of battery packs. Its main functions include:
Monitoring
- It tracks the voltage, current, and temperature of individual cells within the battery pack via cell monitoring units (CMUs) to ensure optimal performance.
Balancing
- The BMU ensures that all cells are charged and discharged evenly, which helps extend battery life and improve efficiency.
Thermal Management
- It manages the temperature of the battery pack using either passive or active cooling methods to prevent overheating.
Fault Detection
- The BMU detects faults and anomalies in the battery system, providing safety measures to prevent failures.
LTSCT BMU ICs are designed to support the layout and functionality of the battery management system (BMS), with careful consideration of charging and discharging requirements of cells and battery packs. These BMU ICs help overcome the challenges of BMS design and contribute to more efficient, longer-lasting, and reliable battery-powered applications.
Key features
High-Performance RISC-V MCU with tight coupling of hardware accelerators
- CORDIC accelerator for Trigonometric, Hyperbolic functions
- 32-bit floating operations using QS11.2 notation
- 32-bit Vector operations
- Neural Network Hardware accelerator blocks such as LSTM, Perceptron, etc.
- Accelerators for both forward and backward propagation
- Modulo-Arithmetic for Authentication
- Performance: CoreMark: 2.47 CoreMark/MHz; Dhrystone: 0.95 DMIPS/MHz
- On-Chip Debug block for debugging the MCU and for measuring the performance
- NVM Scratchpad for customer code
- Capability to support BLE communication from CMU(s) to CMU/BMU along with standard capacitive isolated communication
- CMU/BMU can be trained and configured to operate with any battery chemistry
- Authentication Engine for secure communications
- Hardware Coulomb Counter
Fault Detection such as
- OV, UV, OC, SC
- Insulation Resistance Drop
- Thermal faults such as OT, UT, Temp. gradient
- SoC/SoH errors, SoP exceeds
- Communication and Controller Faults
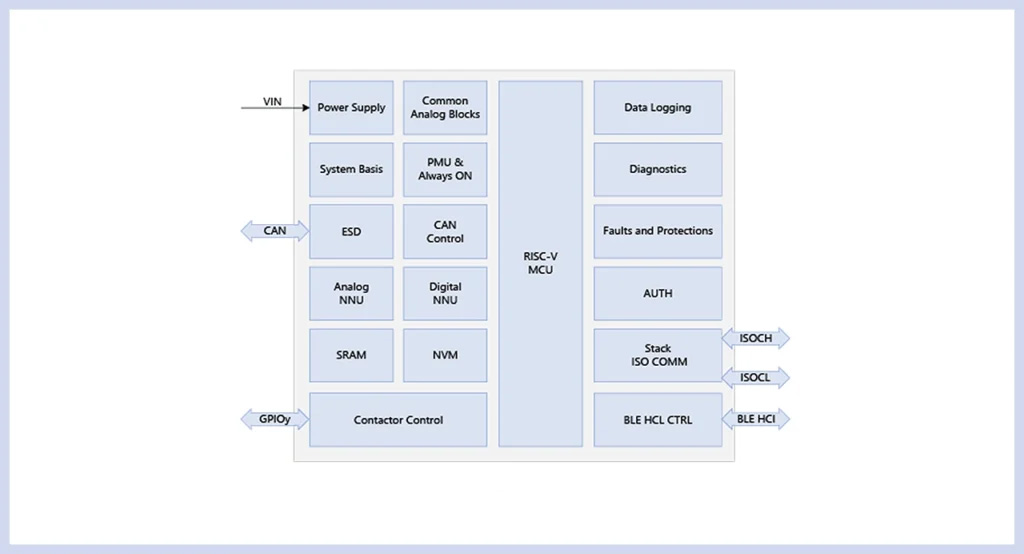
Block diagram
Talk with an expert
We’re always ready to connect with you. Whether it’s feedback, a query, or a partnership opportunity, we’re just a click away.







